Power management is vital for enhancing power rates and making certain optimum power levels are offered for high quality with minimized energy usage.
It is often discovered that many computers are booted with power settings that are overconservative for the primary purpose of decreasing the rate at which battery facilities are used up on portable computers or to minimize heat production by stationary ones.
Although such settings help making the system stable, these may not always prove to be very efficient in terms of performance to power consumption ratio.
Enabling BIOS gives users an opportunity to manage power control settings depending on some particular requirements like:
- Working on P-states & C-states for efficient energy consumption – Current day CPUs and GPUs have provisions for various operational power states to be adjusted according to the working requirements.
This is because, with an unlocked BIOS, you can tweak most of these to reduce power consumption during those moments they are idle while at the same time up their power on challenging moments. - Fan Speed Regulation to Manage Temperature – Some firms design car fans with the intention of regulating noise levels at the expense of the cooling capacity.
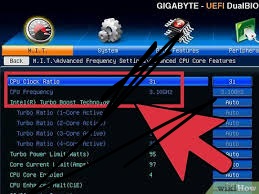
It offers functions such as the BIOS fan speed control that is capable to vary the speed of a particular fan with respect to some parameters of temperature, to avoid over heating the computer and at the same time, with the noise level of a fan. - Turbo Boost and Power Limits – Both Intel and AMD processors have power managing features which include Intel’s Turbo Boost and AMD’s Precision Boost.
Still, when configured to their default, they are not very handy.
Enabling BIOS provides users with the possibility to increase the boost time and the power limit as well as enhance the functioning of CPU.
This makes it possible for users to achieve a system that is more efficient in energy usage while producing high performance and a relatively low generation of heat and power usage.
Reducing System Latency
In the context of game players, programmers and high performance computing the length of time it takes for the system to respond to an issued command is an essential parameter.
Latency refers to the delay between input (such as a mouse click or keyboard press) and the system’s response.
High latency thins downgrade the application’s response time, decreases the real-time capacity of games, and reduces the productivity level and efficiency of other occupations.
Extra low latency settings that are available when unlocked in the BIOS are as follows:
- Enhancing the Performance Through Modifying Memory Timing – RAM timing plays an important role in system performance.
There is a way to manually adjust memory settings and that is by unlocking BIOS; this helps in the reduction of delays when reading and writing to memory for real-time processes. - System Configuration – Using the BIOS, it is possible to set privileged priorities to certain software applications or procedures.
CPU affinity and priority have been known to be set in such a way that important programs are given the required computations. - Uninstalling Unwanted Start-up Programs – Some BIOS options are related to system startup processes – primarily using system start-up options that help to reduce power consumption or perform security scans.
To cut down the input lag and lessen the sluggishness of the system, it is wiser to close clients that are not essential. - Reducing PCIe and USB Latency – USB and PCIe speeds are very fast and are utilized in gaming mice and mechanical keyboards.
Enabling BIOS on your computer allows better configuration of these relations for desired data transfer rate and lessennes input noise.
To the core gamers, any amount of lag could be the thing that costs them the game.
It can therefore be noted that, by adjusting various settings in BIOS, users can gain enhanced response times, enhanced gameplay and enhanced computing.
